스프링 MVC - 웹 페이지 만들기
목차
프로젝트 생성
- 스프링 공식 홈페이지에서 프로젝트 구성 (https://start.spring.io)
- IntelliJ Ultimate 이상이면 자체적으로 생성가능
프로젝트 구성
- 프로젝트 선택
- Project: Gradle - Groovy
- Language: Java
- Sprng Boot: 2.4.x
- Protject MetaData
- Group : hello
- Artifact: springmvc
- Name: springmvc
- Package name: hello.springmvc
- Packaging: Jar
- java: 11
Dependencies
- Spring Web
- Thymeleaf
- Lombok
build.gradle
plugins {
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '2.4.3'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.0.11.RELEASE'
id 'java'
}
group = 'hello'
version = '0.0.1-SNAPSHOT'
sourceCompatibility = '11'
configurations {
compileOnly {
extendsFrom annotationProcessor
}
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
}
test {
useJUnitPlatform()
}
Welcome 페이지 추가
편리하게 사용할 수 있도록 Welcome 페이지를 추가하자.
/resources/static/index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>상품 관리
<ul>
<li><a href="/basic/items">상품 관리 - 기본</a></li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
요구사항 분석
상품을 관리할 수 있는 서비스를 만들어보자.
상품 도메인 모델
- 상품 ID
- 상품명
- 가격
- 수량
상품 관리 기능
- 상품 목록
- 상품 상세
- 상품 등록
- 상품 수정
서비스 화면
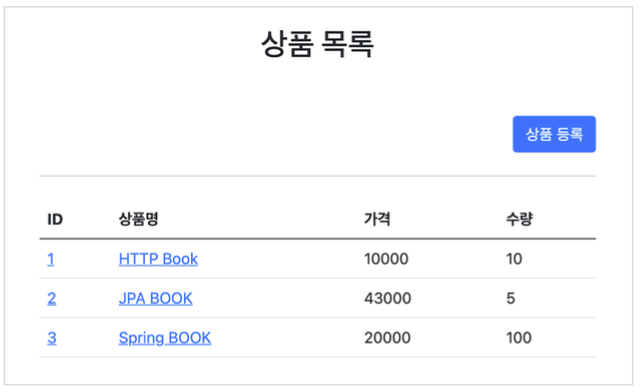
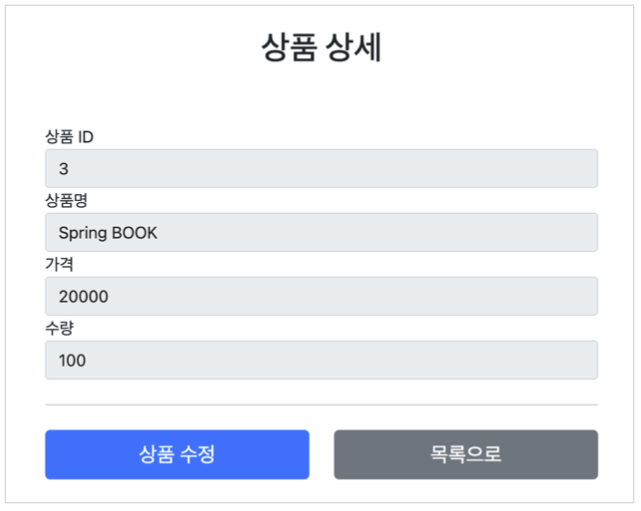
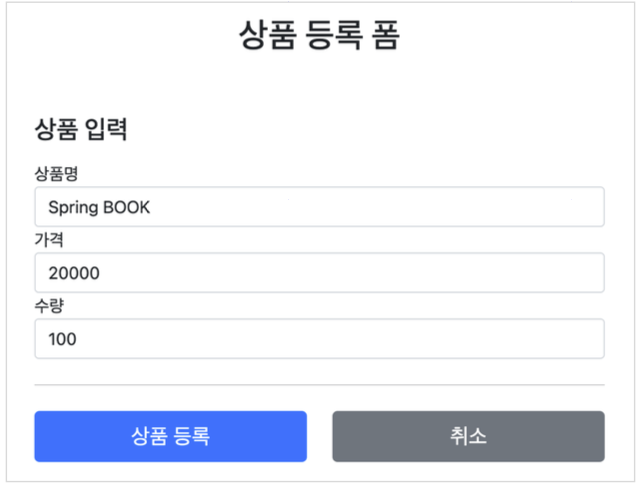
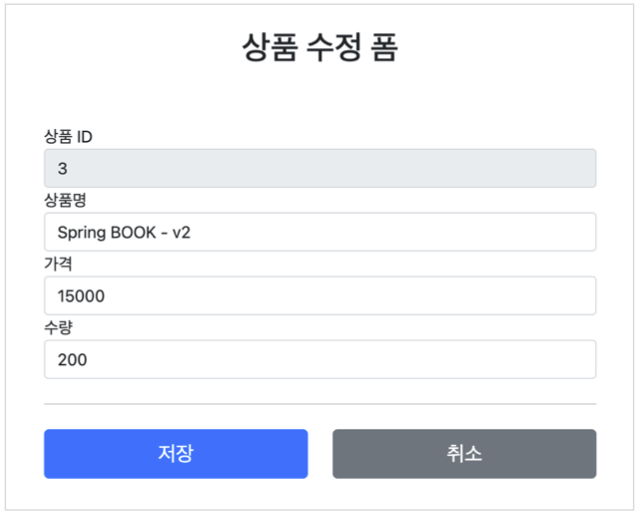
서비스 제공 흐름
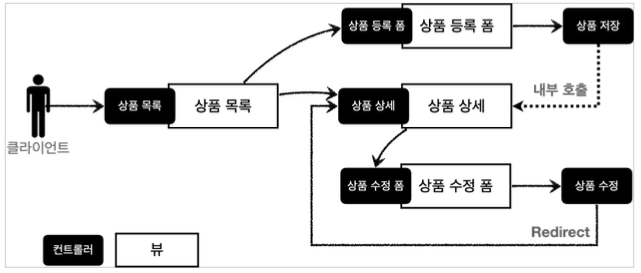
요구사항이 정리되고 디자이너, 웹 퍼블리셔, 백엔드 개발자가 업무를 나누어 진행한다.
- 디자이너: 요구사항에 맞도록 디자인하고, 디자인 결과물을 웹 퍼블리셔에게 넘겨준다.
- 웹 퍼블리셔: 디자이너에서 받은 디자인을 기반으로 HTML, CSS를 만들어 개발자에게 제공한다.
- 백엔드 개발자: 디자이너, 웹 퍼블리셔를 통해서 HTML 화면이 나오기 전까지 시스템을 설계하고, 핵심 비즈니스 모델을 개발한다. 이후 HTML이 나오면 이 HTML을 뷰 템플릿으로 변환해서 동적으로 화면을 그리고, 또 웹 화면의 흐름을 제어한다.
참고
React, Vue.js 같은 웹 클라이언트 기술을 사용하고, 웹 프론트엔드 개발자가 별도로 있으면, 웹 프론트엔드 개발자가 웹 퍼블리셔 역할까지 포함해서 하는 경우도 있다.
웹 클라이언트 기술을 사용하면, 웹 프론트엔드 개발자가 HTML을 동적으로 만드는 역할과 웹 화면의 흐름을 담당한다.
이 경우 백엔드 개발자는 HTML 뷰 템플릿을 직접 만지는 대신에, HTTP API를 통해 웹 클라이언트가 필요로 하는 데이터와 기능을 제공하면 된다.
상품 도메인 개발
Item - 상품 객체
package hello.itemservice.domain.item;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
@Getter
@Setter
public class Item {
private Long id;
private String itemName;
private Integer price;
private Integer quantity;
public Item() {
}
public Item(String itemName, Integer price, Integer quantity) {
this.itemName = itemName;
this.price = price;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
}
ItemRepository - 상품 저장소
package hello.itemservice.domain.item;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class ItemRepository {
private static final Map<Long, Item> store = new HashMap<>(); //static
private static long sequence = 0L; //static
public Item save(Item item) {
item.setId(++sequence);
store.put(item.getId(), item);
return item;
}
public Item findById(Long id) {
return store.get(id);
}
public List<Item> findAll() {
return new ArrayList<>(store.values());
}
public void update(Long itemId, Item updateParam) {
Item findItem = findById(itemId);
findItem.setItemName(updateParam.getItemName());
findItem.setPrice(updateParam.getPrice());
findItem.setQuantity(updateParam.getQuantity());
}
public void clearStore() {
store.clear();
}
}
ItemRepositoryTest - 상품 저장소 테스트
package hello.itemservice.domain.item;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.*;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
class ItemRepositoryTest {
ItemRepository itemRepository = new ItemRepository();
@AfterEach
void afterEach() {
itemRepository.clearStore();
}
@Test
public void save() throws Exception {
//given
Item item = new Item("itemA", 10000, 10);
//when
Item saveItem = itemRepository.save(item);
//then
Item findItem = itemRepository.findById(item.getId());
assertThat(findItem).isEqualTo(saveItem);
}
@Test
public void findAll() throws Exception {
//given
Item item1 = new Item("item1", 10000, 10);
Item item2 = new Item("item2", 20000, 20);
itemRepository.save(item1);
itemRepository.save(item2);
//when
List<Item> result = itemRepository.findAll();
//then
assertThat(result.size()).isEqualTo(2);
assertThat(result).contains(item1, item2);
}
@Test
public void updateItem() throws Exception {
//given
Item item = new Item("item", 10000, 10);
Item savedItem = itemRepository.save(item);
Long itemId = savedItem.getId();
//when
Item updateParam = new Item("item2", 20000, 30);
itemRepository.update(itemId, updateParam);
//then
Item findItem = itemRepository.findById(itemId);
assertThat(findItem.getItemName()).isEqualTo(updateParam.getItemName());
assertThat(findItem.getPrice()).isEqualTo(updateParam.getPrice());
assertThat(findItem.getQuantity()).isEqualTo(updateParam.getQuantity());
}
}
상품 서비스 HTML
핵심 비즈니스 로직을 개발하는 동안, 웹 퍼블리셔는 HTML 마크업을 완료했다.
다음 파일들을 경로에 잘 넣고 동작하는지 확인해보자.
부트스트랩
참고로 HTML을 편리하기 개발하기 위해 부트스트랩 사용했다.
먼저 필요한 부트스트랩 파일을 설치하자
- 부트스트랩 공식 사이트: http://getbootstrap.com
Bootstrap
Powerful, extensible, and feature-packed frontend toolkit. Build and customize with Sass, utilize prebuilt grid system and components, and bring projects to life with powerful JavaScript plugins.
getbootstrap.com
- 부트스트랩을 다운로드 받고 압축을 풀자.
- 이동: https://getbootstrap.com/docs/5.0/getting-started/download/
- Compiled CSS and JS 항목을 다운로드하자.
- 압축을 풀고 bootstrap.min.css를 복사해서 다음 폴더에 추가하자
- resources/static/css/bootstrap.min.css
참고
부트스트랩(Bootstrap)은 웹사이트를 쉽게 만들 수 있게 도와주는 HTML, CSS, JS 프레임워크이다.
하나의 CSS로 휴대폰, 태블릿, 데스크탑까지 다양한 기기에서 작동한다. 다양한 기능을 제공하여 사용자가 쉽게 웹사이트를 제작, 유지, 보수할 수 있도록 도와준다. -출처: 위키백과
HTML, css 파일
- /resources/static/css/bootstrap.min.css -> 부트스트랩 다운로드
- /resources/static/html/items.html -> 아래 참조
- /resources/static/html/item.html
- /resources/static/html/addForm.html
- /resources/static/html/editForm.html
참고로 /resources/static 에 넣어두었기 때문에 스프링 부트가 정적 리소스를 제공한다.
http://localhost:8080/html/items.html
그런데 정적 리소스여서 해당 파일을 탐색기를 통해 직접 열어도 동작하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
상품 목록 HTML
resources/static/html/items.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<link href="../css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container" style="max-width: 600px">
<div class="py-5 text-center">
<h2>상품 목록</h2>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
<button class="btn btn-primary float-end"
onclick="location.href='addForm.html'" type="button">상품 등록</button>
</div>
</div>
<hr class="my-4">
<div>
<table class="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>상품명</th>
<th>가격</th>
<th>수량</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td><a href="item.html">1</a></td>
<td><a href="item.html">테스트 상품1</a></td>
<td>10000</td>
<td>10</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><a href="item.html">2</a></td>
<td><a href="item.html">테스트 상품2</a></td>
<td>20000</td>
<td>20</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div> <!-- /container -->
</body>
</html>
상품 상세 HTML
resources/static/html/item.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<link href="../css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<style>
.container {
max-width: 560px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="py-5 text-center">
<h2>상품 상세</h2>
</div>
<div>
<label for="itemId">상품 ID</label>
<input type="text" id="itemId" name="itemId" class="form-control" value="1" readonly>
</div>
<div>
<label for="itemName">상품명</label>
<input type="text" id="itemName" name="itemName" class="form-control" value="상품A" readonly>
</div>
<div>
<label for="price">가격</label>
<input type="text" id="price" name="price" class="form-control" value="10000" readonly>
</div>
<div>
<label for="quantity">수량</label>
<input type="text" id="quantity" name="quantity" class="form-control" value="10" readonly>
</div>
<hr class="my-4">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
<button class="w-100 btn btn-primary btn-lg" onclick="location.href='editForm.html'" type="button">상품 수정</button>
</div>
<div class="col">
<button class="w-100 btn btn-secondary btn-lg" onclick="location.href='items.html'" type="button">목록으로</button>
</div>
</div>
</div> <!-- /container -->
</body>
</html>
상품 등록 폼 HTML
resources/static/html/addForm.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<link href="../css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<style>
.container {
max-width: 560px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="py-5 text-center">
<h2>상품 등록 폼</h2>
</div>
<h4 class="mb-3">상품 입력</h4>
<form action="item.html" method="post">
<div>
<label for="itemName">상품명</label>
<input type="text" id="itemName" name="itemName" class="form-control" placeholder="이름을 입력하세요">
</div>
<div>
<label for="price">가격</label>
<input type="text" id="price" name="price" class="form-control" placeholder="가격을 입력하세요">
</div>
<div>
<label for="quantity">수량</label>
<input type="text" id="quantity" name="quantity" class="form-control" placeholder="수량을 입력하세요">
</div>
<hr class="my-4">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
<button class="w-100 btn btn-primary btn-lg" type="submit">상품 등록</button>
</div>
<div class="col">
<button class="w-100 btn btn-secondary btn-lg" onclick="location.href='items.html'" type="button">취소</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div> <!-- /container -->
</body>
</html>
상품 수정 폼 HTML
resources/static/html/editForm.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<link href="../css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<style>
.container {
max-width: 560px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="py-5 text-center">
<h2>상품 수정 폼</h2>
</div>
<form action="item.html" method="post">
<div>
<label for="id">상품 ID</label>
<input type="text" id="id" name="id" class="form-control" value="1" readonly>
</div>
<div>
<label for="itemName">상품명</label>
<input type="text" id="itemName" name="itemName" class="form-control" value="상품A">
</div>
<div>
<label for="price">가격</label>
<input type="text" id="price" name="price" class="form-control" value="10000">
</div>
<div>
<label for="quantity">수량</label>
<input type="text" id="quantity" name="quantity" class="form-control" value="10">
</div>
<hr class="my-4">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
<button class="w-100 btn btn-primary btn-lg" type="submit">저장</button>
</div>
<div class="col">
<button class="w-100 btn btn-secondary btn-lg" onclick="location.href='item.html'" type="button">취소</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div> <!-- /container -->
</body>
</html>
상품 목록 - 타임리프
본격적으로 컨트롤러와 뷰 템플릿을 개발해보자.
BasicItemController
package hello.itemservice.web.basic;
import hello.itemservice.domain.item.Item;
import hello.itemservice.domain.item.ItemRepository;
import java.util.List;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/basic/items")
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class ItemController {
private final ItemRepository itemRepository;
@GetMapping
public String items(Model model) {
List<Item> items = itemRepository.findAll();
model.addAttribute("items", items);
return "basic/items";
}
/**
* 테스트용 데이터 추가
*/
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
itemRepository.save(new Item("itemA", 10000, 10));
itemRepository.save(new Item("itemB", 20000, 20));
}
}
컨트롤러 로직은 ItemRepository에서 모든 상품을 조회한 다음에 모델에 담는다. 그리고 뷰 템플릿을 호출한다.
@RequiredArgsContructor
- final이 붙은 멤버변수만 사용해서 생성자를 자동으로 만들어준다.
public BasicItemController(ItemRepository itemRepository) {
this.itemRepository = itemRepository;
}
- 이렇게 생성자가 딱 1개만 있으면 스프링이 해당 생성자에 @Autowired로 의존관계를 주입해준다.
- 따라서 final 키워드를 빼면 안된다!, 그러면 ItemRepository 의존관계 주입이 안된다.
- 스프링 핵심원리 - 기본편 강의 참고
테스트용 데이터 추가
- 테스트용 데이터가 없으면 회원 목록 기능이 정상 동작하는지 확인하기 어렵다.
- @PostConstruct: 해당 빈의 의존관계가 모두 주입되고 나면 초기화 용도로 호출된다.
- 여기서는 간단히 테스트용 데이터를 넣기 위해서 사용했다.
item.html 정적 HTML을 뷰 템플릿(templates)영역으로 복사하고 다음과 같이 수정하자
/resources/static/items.html -> /resources/templates/basic/items.html
/resources/templates/basic/items.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<link th:href="@{/css/bootstrap.min.css}"
href="../css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container" style="max-width: 600px">
<div class="py-5 text-center">
<h2>상품 목록</h2>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
<button class="btn btn-primary float-end"
onclick="location.href='addForm.html'"
th:onclick="|location.href='@{/basic/items/add}'|"
type="button">상품 등록</button>
</div>
</div>
<hr class="my-4">
<div>
<table class="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>상품명</th>
<th>가격</th>
<th>수량</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="item : ${items}">
<td><a href="item.html" th:href="@{/basic/items/{itemId}(itemId=${item.id})}" th:text="${item.id}">회원 id</a></td>
<td><a href="item.html" th:href="@{/basic/items/{itemId}(itemId=${item.id})}" th:text="${item.itemName}">상품명</a></td>
<td th:text="${item.price}">10000</td>
<td th:text="${item.quantity}">10</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div> <!-- /container -->
</body>
</html>
타임리프 간단히 알아보기
타임리프 사용 선언
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
속성 변경 - th:href
th:href="@{/css/bootstrap.min.css}"
- href="value1"을 th:href="value2"의 값으로 변경한다.
- 타임리프 뷰 템플릿을 거치게 되면 원래 값을 th:xxx 값으로 변경한다. 만약 값이 없다면 새로 생성한다.
- HTML을 그대로 볼 때는 href 속성이 사용되고, 뷰 템플릿을 거치면 th:href의 값이 href로 대체되면서 동적으로 변경할 수 있다.
- 대부분의 HTML 속성을 th:xxx로 변경할 수 있다.
타임리프 핵심
- 핵심은 th:xxx가 붙은 부분은 서버사이드에서 렌더링 되고, 기존 것을 대체한다. th:xxx이 없으면 기존 html의 xxx속성이 그대로 사용된다.
- HTML을 파일로 직접 열었을 때, th:xxx가 있어도 웹 브라우저는 th: 속성을 알지 못하므로 무시한다.
- 따라서 HTML을 파일 보기를 하면 유지하면서 템플릿 기능도 할 수 있다.
URL 링크 표현식 - @{...}
th:href="@{/css/bootstrap.min.css}"
- @{...}: 타임리프는 URL 링크를 사용하는 경우 @{...}를 사용한다. 이것을 URL 링크 표현식이라 한다.
- URL 링크 표현식을 사용하면 서블릿 컨텍스트를 자동으로 포함한다.
상품 등록 폼으로 이동
속성 변경 - th:onclick
- onclick="location.href='addForm.html'"
- th:onclick="|location.href='@{/basic/items/add}'|"
여기에는 다음에 설명하는 리터럴 대체 문법이 사용되었다. 자세히 알아보자.
리터럴 대체 - |...|
|...| :이렇게 사용한다.
- 타임리프에서 문자와 표현식 등은 분리되어 있기 때문에 더해서 사용해야 한다.
- <span th:text="'Welcome to our application, ' + ${user.name} + '!'">
- 다음과 같이 리터럴 대체 문법을 사용하면, 더하기 없이 편리하게 사용할 수 있다.
- <span th:text="|Welcome to our application, ${user.name}!|">
- 결과를 다음과 같이 만들어야 하는데
- location.href='/basic/items/add'
- 그냥 사용하면 문자와 표현식을 각각 따로 더해서 사용해야 하므로 다음과 같이 복잡해진다.
- th:onclick="'location.href=' + '\'' + @{/basic/items/add} + '\''"
- 리터럴 대체 문법을 사용하면 다음과 같이 편리하게 사용할 수 있다.
- th:onclick="|location.href='@{/basic/items/add}'|"
반복 출력 - th:each
- <tr th:each="item : ${items}">
- 반복은 th:each 를 사용한다. 이렇게 하면 모델에 포함된 items 컬렉션 데이터가 item 변수에 하나씩 포함되고, 반복문 안에서 item 변수를 사용할 수 있다.
- 컬렉션의 수 만큼 <tr>..</tr> 이 하위 테그를 포함해서 생성된다.
변수 표현식 - ${...}
- <td th:text="${item.price}">10000</td>
- 모델에 포함된 값이나, 타임리프 변수로 선언한 값을 조회할 수 있다.
- 프로퍼티 접근법을 사용한다. ( item.getPrice() )
내용 변경 - th:text
- <td th:text="${item.price}">10000</td>
- 내용의 값을 th:text 의 값으로 변경한다.
- 여기서는 10000을 ${item.price} 의 값으로 변경한다.
URL 링크 표현식2 - @{...},
- th:href="@{/basic/items/{itemId}(itemId=${item.id})}"
- 상품 ID를 선택하는 링크를 확인해보자.
- URL 링크 표현식을 사용하면 경로를 템플릿처럼 편리하게 사용할 수 있다.
- 경로 변수( {itemId} ) 뿐만 아니라 쿼리 파라미터도 생성한다.
- 예) th:href="@{/basic/items/{itemId}(itemId=${item.id}, query='test')}"
- 생성 링크: http://localhost:8080/basic/items/1?query=test
URL 링크 간단히
- th:href="@{|/basic/items/${item.id}|}"
- 상품 이름을 선택하는 링크를 확인해보자.
- 리터럴 대체 문법을 활용해서 간단히 사용할 수도 있다.
참고
타임리프는 순수 HTML 파일을 웹 브라우저에서 열어도 내용을 확인할 수 있고, 서버를 통해 뷰 템플릿을 거치면 동적으로 변경된 결과를 확인할 수 있다. JSP를 생각해보면, JSP 파일은 웹 브라우저에서 그냥 열면 JSP 소스코드와 HTML이 뒤죽박죽 되어서 정상적인 확인이 불가능하다. 오직 서버를 통해서 JSP를 열어야 한다.
이렇게 순수 HTML을 그대로 유지하면서 뷰 템플릿도 사용할 수 있는 타임리프의 특징을 네츄럴 템플릿 (natural templates) 이라 한다
상품 상세
상품 상세 컨트롤러와 뷰를 개발하자.
BasicItemController에 추가
@GetMapping("/{itemId}")
public String item(@PathVariable Long itemId, Model model) {
Item item = itemRepository.findById(itemId);
model.addAttribute("item", item);
return "basic/item";
}PathVariable 로 넘어온 상품ID로 상품을 조회하고, 모델에 담아둔다. 그리고 뷰 템플릿을 호출한다.
상품 상세 뷰
정적 HTML을 뷰 템플릿(templates) 영역으로 복사하고 다음과 같이 수정하자.
/resources/static/item.html -> /resources/templates/basic/item.html
/resources/templates/basic/item.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<link th:href="@{/css/bootstrap.min.css}"
href="../css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<style>
.container {
max-width: 560px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="py-5 text-center">
<h2>상품 상세</h2>
</div>
<div>
<label for="itemId">상품 ID</label>
<input type="text" id="itemId" name="itemId" class="form-control" value="1" th:value="${item.id}" readonly>
</div>
<div>
<label for="itemName">상품명</label>
<input type="text" id="itemName" name="itemName" class="form-control" value="상품A" th:value="${item.itemName}" readonly>
</div>
<div>
<label for="price">가격</label>
<input type="text" id="price" name="price" class="form-control" value="10000" th:value="${item.price}" readonly>
</div>
<div>
<label for="quantity">수량</label>
<input type="text" id="quantity" name="quantity" class="form-control" value="10" th:value="${item.quantity}" readonly>
</div>
<hr class="my-4">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
<button class="w-100 btn btn-primary btn-lg"
onclick="location.href='editForm.html'"
th:onclick="|location.href='@{/basic/items/{itemId}/edit(itemId=${item.id})}'|"
type="button">상품 수정</button>
</div>
<div class="col">
<button class="w-100 btn btn-secondary btn-lg"
onclick="location.href='items.html'"
th:onclick="|location.href='@{/basic/items}'|"
type="button">목록으로</button>
</div>
</div>
</div> <!-- /container -->
</body>
</html>
속성 변경 - th:value
th:value="${item.id}"
- 모델에 있는 item 정보를 획득하고 프로퍼티 접근법으로 출력한다. ( item.getId() )
- value 속성을 th:value 속성으로 변경한다.
상품수정 링크
- th:onclick="|location.href='@{/basic/items/{itemId}/edit(itemId=${item.id})}'|"
목록으로 링크
- th:onclick="|location.href='@{/basic/items}'|"
상품 등록 폼
상품 등록 폼
BasicItemController에 추가
@GetMapping("/add")
public String addForm() {
return "basic/addForm";
}상품 등록 폼은 단순히 뷰 템플릿만 호출한다.
상품 등록 폼 뷰
정적 HTML을 뷰 템플릿(templates) 영역으로 복사하고 다음과 같이 수정하자.
/resources/static/addForm.html -> /resources/templates/basic/addForm.html
/resources/templates/basic/addForm.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<link th:href="@{/css/bootstrap.min.css}"
href="../css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<style>
.container {
max-width: 560px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="py-5 text-center">
<h2>상품 등록 폼</h2>
</div>
<h4 class="mb-3">상품 입력</h4>
<form action="item.html" th:action method="post">
<div>
<label for="itemName">상품명</label>
<input type="text" id="itemName" name="itemName" class="form-control" placeholder="이름을 입력하세요">
</div>
<div>
<label for="price">가격</label>
<input type="text" id="price" name="price" class="form-control" placeholder="가격을 입력하세요">
</div>
<div>
<label for="quantity">수량</label>
<input type="text" id="quantity" name="quantity" class="form-control" placeholder="수량을 입력하세요">
</div>
<hr class="my-4">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
<button class="w-100 btn btn-primary btn-lg" type="submit">상품 등록</button>
</div>
<div class="col">
<button class="w-100 btn btn-secondary btn-lg"
onclick="location.href='items.html'"
th:onclick="|location.href='@{/basic/items}'|"
type="button">취소</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div> <!-- /container -->
</body>
</html>
속성 변경 - th:action
- th:action
- HTML form에서 action에 값이 없으면 현재 URL에 데이터를 전송한다.
- 상품 등록 폼의 URL과 실제 상품 등록을 처리하는 URL을 똑같이 맞추고 HTTP 메서드로 두 기능을 구분한다.
- 상품 등록 폼: GET /basic/items/add
- 상품 등록 처리: POST /basic/items/add
- 이렇게 하면 하나의 URL로 등록 폼과, 등록 처리를 깔끔하게 처리할 수 있다.
취소
- 취소시 상품 목록으로 이동한다.
- th:onclick="|location.href='@{/basic/items}|"
상품 등록 처리 - @ModelAttribute
이제 상품 등록 폼에서 전달된 데이터로 실제 상품을 등록 처리해보자.
상품 등록 폼은 다음 방식으로 서버에 데이터를 전달한다.
- POST - HTML Form
- content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- 메시지 바디에 쿼리 파라미터 형식으로 전달 itemName=itemA&price=10000&quantity=10
- 예) 회원 가입, 상품 주문, HTML Form 사용
요청 파라미터 형식을 처리해야 하므로 @RequestParam을 사용하자
상품 등록 처리 - @RequestParam
addItemV1 - basicItemController에 추가
@PostMapping("/add")
public String addItemV1(
@RequestParam String itemName,
@RequestParam int price,
@RequestParam Integer quantity,
Model model) {
Item item = new Item();
item.setItemName(itemName);
item.setPrice(price);
item.setQuantity(quantity);
itemRepository.save(item);
model.addAttribute("item", item);
return "basic/item";
}- 먼저 @RequestParam String itemName: itemName 요청 파라미터 데이터를 해당 변수에 받는다.
- Item 객체를 생성하고 itemRepository를 통해서 저장한다.
- 저장된 item에 모델을 담아서 뷰에 전달한다.
중요: 여기서는 상품 상세에서 사용한 item.html 뷰 템플릿을 그대로 재활용한다.
실행해서 상품이 잘 저장되는지 확인하자.
상품 등록 처리 - @ModelAttribute
@RequestParam으로 변수를 하나하나 받아서 Item을 생성하는 과정은 불편했다.
이번에는 @ModelAttribute를 사용해서 한번에 처리해보자.
addItemV2 - 상품 등록 처리 - ModelAttribute
/**
* @ModelAttribute("item") Item item
* model.addAttribute("item", item); 자동 추가
* */
@PostMapping("/add")
public String addItemV2(@ModelAttribute("item") Item item, Model model) {
itemRepository.save(item);
//model.addAttribute("item", item); //자동 추가, 생략 가능
return "basic/item";
}
@ModelAttribute - 요청 파라미터 처리
@ModelAttribute는 Item객체를 생성하고, 요청 파라미터의 값을 프로퍼티 접근법(setXxx)으로 입력해준다.
@ModelAttribute - Model 추가
@ModelAttribute는 중요한 한가지 기능이 더 있는데, 바로 모델(Model)에 @ModelAttribute로 지정한 객체를 자동으로 넣어준다. 지금 코드를 보면 model.addAttribute("item", item)가 주석처리 되어 있어도 잘 동작하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
모델에 데이터를 담을 때는 이름이 필요하다. 이름은 @ModelAttribute에 지정한 name(value) 속성을 사용한다. 만약 다음과 같이 @ModelAttribute의 이름을 다르게 지정하면 다른 이름으로 모델에 포함된다.
@ModelAttribute("hello") Item item -> 이름을 hello로 지정
model.addAttribute("hello", item); -> 모델에 Hello이름으로 저장
주의
실행전에 이전 버전인 addItemV1에 @PostMapping("/add")를 꼭 주석처리 해주어야 한다. 그렇지 않으면 중복 매핑으로 오류가 발생한다.
//@PostMapping("/add") 이전 코드의 매핑 주석처리!
public String addItemV1(@RequestParam String itemName,
addItemV3 - 상품 등록 처리 - ModelAttribute 이름 생략
/**
* @ModelAttribute name 생략 가능
* model.addAttribute(item); 자동 추가, 생략 가능
* 생략시 model에 저장되는 name은 클래스명 첫글자만 소문자로 등록 Item -> item
*/
@PostMapping("/add")
public String addItemV3(@ModelAttribute Item item) {
itemRepository.save(item);
return "basic/item";
}@ModelAttribute 의 이름을 생략할 수 있다.
주의
@ModelAttribute 의 이름을 생략하면 모델에 저장될 때 클래스명을 사용한다. 이때 클래스의 첫글자만 소문자로 변경해서 등록한다.
- 예) @ModelAttribute 클래스명 -> 모델에 자동 추가되는 이름
- Item -> item
- HelloWorld -> helloWorld
addItemV4 - 상품 등록 처리 - ModelAttribute 전체 생략
/**
* @ModelAttribute 자체 생략 가능
* model.addAttribute(item) 자동 추가
*/
@PostMapping("/add")
public String addItemV4(Item item) {
itemRepository.save(item);
return "basic/item";
}@ModelAttribute 자체도 생략가능하다. 대상 객체는 모델에 자동 등록된다. 나머지 사항은 기존과 동일하다.
상품 수정
상품 수정 폼 컨트롤러
BasicItemController에 추가
@GetMapping("/{itemId}/edit")
public String editForm(@PathVariable Long itemId, Model model) {
Item item = itemRepository.findById(itemId);
model.addAttribute("item", item);
return "basic/editForm";
}수정에 필요한 정보를 조회하고, 수정용 폼 뷰를 호출한다.
상품 수정 폼 뷰
정적 HTML을 뷰 템플릿(templates) 영역으로 복사하고 다음과 같이 수정하자.
/resources/static/editForm.html -> /resources/templates/basic/editForm.html
/resources/templates/basic/editForm.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<link th:href="@{/css/bootstrap.min.css}"
href="../css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<style>
.container {
max-width: 560px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="py-5 text-center">
<h2>상품 수정 폼</h2>
</div>
<form action="item.html" th:action method="post">
<div>
<label for="id">상품 ID</label>
<input type="text" id="id" name="id" class="form-control" value="1" th:value="${item.id}"readonly>
</div>
<div>
<label for="itemName">상품명</label>
<input type="text" id="itemName" name="itemName" class="form-control" th:value="${item.itemName}" value="상품A">
</div>
<div>
<label for="price">가격</label>
<input type="text" id="price" name="price" class="form-control" value="10000" th:value="${item.price}">
</div>
<div>
<label for="quantity">수량</label>
<input type="text" id="quantity" name="quantity" class="form-control" value="10" th:value="${item.quantity}">
</div>
<hr class="my-4">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
<button class="w-100 btn btn-primary btn-lg" type="submit">저장</button>
</div>
<div class="col">
<button class="w-100 btn btn-secondary btn-lg"
onclick="location.href='item.html'"
th:onclick="|location.href='@{/basic/items/{itemId}(itemId=${item.id})}'|"
type="button">취소</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div> <!-- /container -->
</body>
</html>상품 수정 폼은 상품 등록과 유사하고, 특별한 내용이 없다.
상품 수정 개발
@PostMapping("/{itemId}/edit")
public String edit(@PathVariable Long itemId, @ModelAttribute Item item) {
itemRepository.update(itemId, item);
return "redirect:/basic/items/{itemId}";
}상품 수정은 상품 등록과 전체 프로세스가 유사하다.
- GET /items/{itemId}/edit: 상품수정폼
- POST /items/{itemId}/edit : 상품 수정 처리
리다이렉트
상품 수정은 마지막에 뷰 템플릿을 호출하는 대신에 상품 상세 화면으로 이동하도록 리다이렉트를 호출한다.
- 스프링은 redirect:/... 으로 편리하게 리다이렉트를 지원한다.
- redirect:/basic/items/{itemId}
- 컨트롤러에 매핑된 @PathVariable 의 값은 redirect 에도 사용 할 수 있다.
- redirect:/basic/items/{itemId} -> {itemId} 는 @PathVariable Long itemId 의 값을 그대로 사용한다.
참고
HTML Form 전송은 PUT, PATCH를 지원하지 않는다. GET, POST만 사용할 수 있다.
PUT, PATCH는 HTTP API 전송시에 사용
스프링에서 HTTP POST로 Form 요청할 때 히든 필드를 통해서 PUT, PATCH 매핑을 사용하는 방법이 있지만, HTTP 요청상 POST 요청이다.
PRG Post/Redirect/Get
사실 지금까지 진행한 상품 등록 처리 컨트롤러는 심각한 문제가 있다.(addItemV1 ~ addItemV4)
상품 등록을 완료하고 웹 브라우저의 새로고침 버튼을 클릭해보자.
상품이 계속해서 중복 등록되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
전체 흐름
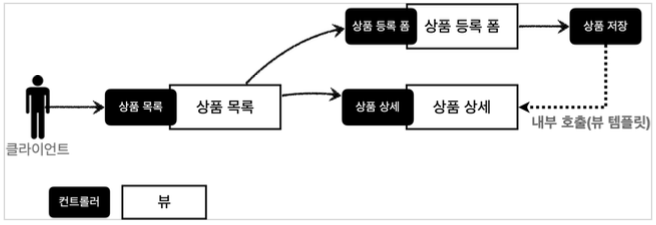
그 이유는 다음 그림을 통해서 확인할 수 있다.
POST 등록 후 새로 고침
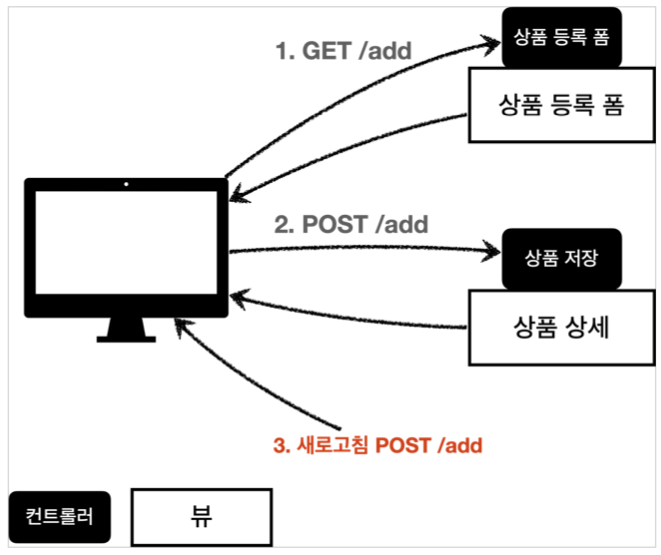
웹 브라우저의 새로 고침은 마지막에 서버에 전송한 데이터를 다시 전송한다.
상품 등록 폼에서 데이터를 입력하고 저장을 선택하면 POST /add + 상품 데이터를 서버로 전송한다.
이 상태에서 새로 고침을 또 선택하면 마지막에 전송한 POST /add + 상품 데이터를 서버로 다시 전송하게 된다.
그래서 내용은 같고, ID만 다른 상품 데이터가 계속 쌓이게 된다.
이 문제를 어떻게 해결할 수 있을까? 다음 그림을 보자.
POST, Redirect GET
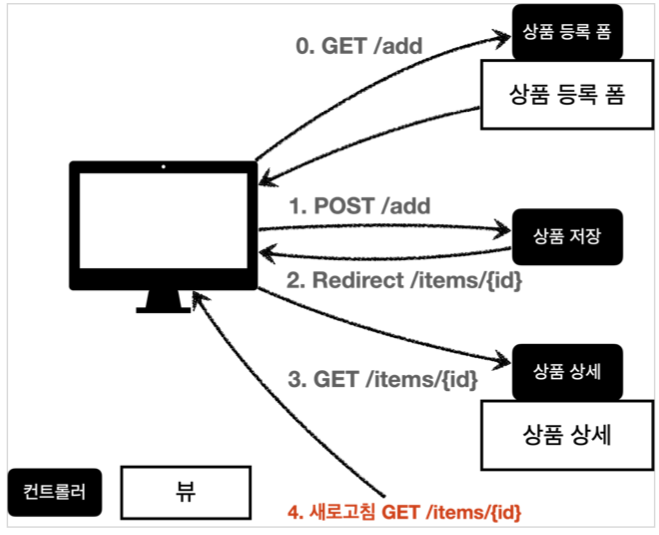
웹 브라우저의 새로 고침은 마지막에 서버에 전송한 데이터를 다시 전송한다.
새로 고침 문제를 해결하려면 상품 저장 후에 뷰 템플릿으로 이동하는 것이 아니라, 상품 상세 화면으로 리다이렉트를 호출해주면 된다.
웹 브라우저는 리다이렉트의 영향으로 상품 저장 후에 실제 상품 상세 화면으로 다시 이동한다. 따라서 마지막에 호출한 내용이 상품 상세 화면인 GET /item/{id}가 되는 것이다.
이후 새로고침을 해도 상품 상세 화면으로 이동하게 되므로 새로 고침 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
BasicItemController에 추가
/**
* PRG - Post/Redirect/Get
*/
@PostMapping("/add")
public String addItemV5(Item item) {
itemRepository.save(item);
return "redirect:/basic/items/" + item.getId();
}상품 등록 처리 이후에 뷰 템플릿이 아니라 상품 상세 화면으로 리다이렉트 하도록 코드를 작성해보자. 이런 문제 해결 방식을 PRG Post/Redirect/Get 라 한다.
주의
"redirect:/basic/items/" + item.getId() redirect에서 +item.getId() 처럼 URL에 변수를 더해서 사용하는 것은 URL 인코딩이 안되기 때문에 위험하다. 다음에 설명하는 RedirectAttributes 를 사용하자.
RedirectAttributes
상품을 저장하고 상품 상세 화면으로 리다이렉트 한 것 까지는 좋았다. 그런데 고객 입장에서 저장이 잘 된 것인지 안 된 것인지 확신이 들지 않는다. 그래서 저장이 잘 되었으면 상품 상세 화면에 "저장되었습니다"라는 메시지를 보여달라는 요구사항이 왔다. 간한하게 해결해보자.
BasicItemController에 추가
/**
* RedirectAttributes
*/
@PostMapping("/add")
public String addItemV6(Item item, RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes) {
Item saveItem = itemRepository.save(item);
redirectAttributes.addAttribute("itemId", saveItem.getId());
redirectAttributes.addAttribute("status", true);
return "redirect:/basic/items/{itemId}";
}
리다이렉트 할 때 간단히 status=true 를 추가해보자. 그리고 뷰 템플릿에서 이 값이 있으면, 저장되었습니다. 라는 메시지를 출력해보자.
실행해보면 다음과 같은 리다이렉트 결과가 나온다.
http://localhost:8080/basic/items/3?status=true
RedirectAttributes
RedirectAttributes 를 사용하면 URL 인코딩도 해주고, pathVarible , 쿼리 파라미터까지 처리해준다.
- redirect:/basic/items/{itemId}
- pathVariable 바인딩: {itemId}
- 나머지는 쿼리 파라미터로 처리: ?status=true
뷰 템플릿 메시지 추가
resources/templates/basic/item.html
<div class="container">
<div class="py-5 text-center">
<h2>상품 상세</h2>
</div>
<!-- 추가 -->
<h2 th:if="${param.status}" th:text="'저장 완료!'"></h2>
- th:if : 해당 조건이 참이면 실행
- ${param.status} : 타임리프에서 쿼리 파라미터를 편리하게 조회하는 기능
- 원래는 컨트롤러에서 모델에 직접 담고 값을 꺼내야 한다. 그런데 쿼리 파라미터는 자주 사용해서 타임리프에서 직접 지원한다.
뷰 템플릿에 메시지를 추가하고 실행해보면 "저장 완료!" 라는 메시지가 나오는 것을 확인할 수 있다. 물론 상품 목록에서 상품 상세로 이동한 경우에는 해당 메시지가 출력되지 않는다.
출처: 인프런 - 스프링 MVC 1편 - 백엔드 웹 개발 핵심 기술
참고
- https://blog.naver.com/allkanet72/220964699929
- https://blog.csdn.net/qq_31230529/article/details/48652061